Structural insight into mechanism and diverse substrate selection strategy of L-ribulokinase.
Agarwal, R., Burley, S.K., Swaminathan, S.(2012) Proteins 80: 261-268
- PubMed: 22072612
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.23202
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
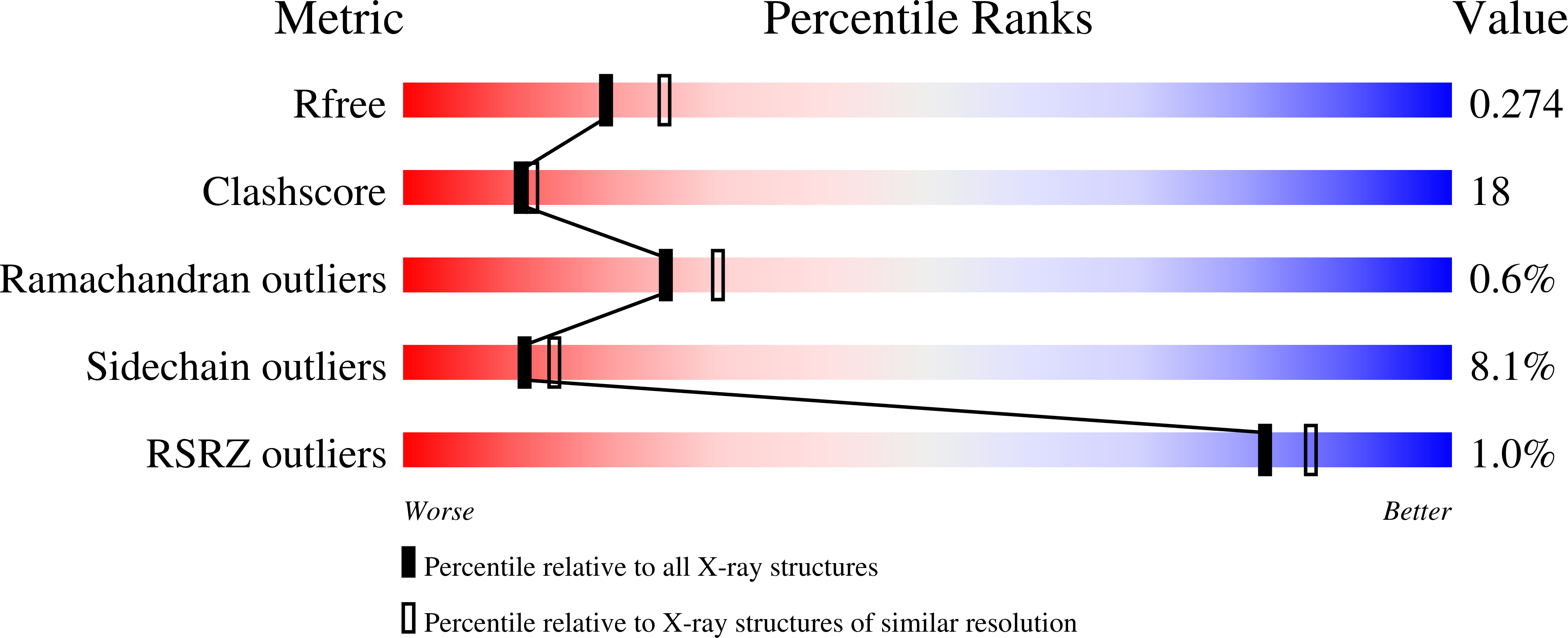
3QDK - PubMed Abstract:
The araBAD operon encodes three different enzymes required for catabolism of L-arabinose, which is one of the most abundant monosaccharides in nature. L-ribulokinase, encoded by the araB gene, catalyzes conversion of L-ribulose to L-ribulose-5-phosphate, the second step in the catabolic pathway. Unlike other kinases, ribulokinase exhibits diversity in substrate selectivity and catalyzes phosphorylation of all four 2-ketopentose sugars with comparable k(cat) values. To understand ribulokinase recognition and phosphorylation of a diverse set of substrates, we have determined the X-ray structure of ribulokinase from Bacillus halodurans bound to L-ribulose and investigated its substrate and ATP co-factor binding properties. The polypeptide chain is folded into two domains, one small and the other large, with a deep cleft in between. By analogy with related sugar kinases, we identified (447)GGLPQK(452) as the ATP-binding motif within the smaller domain. L-ribulose binds in the cleft between the two domains via hydrogen bonds with the side chains of highly conserved Trp126, Lys208, Asp274, and Glu329 and the main chain nitrogen of Ala96. The interaction of L-ribulokinase with L-ribulose reveals versatile structural features that help explain recognition of various 2-ketopentose substrates and competitive inhibition by L-erythrulose. Comparison of our structure to that of the structures of other sugar kinases revealed conformational variations that suggest domain-domain closure movements are responsible for establishing the observed active site environment.
Organizational Affiliation:
Biology Department, Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, New York 11973, USA.