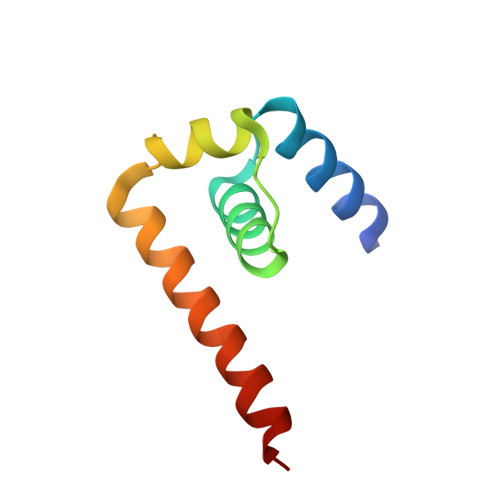
West nile virus core protein; tetramer structure and ribbon formation
Dokland, T., Walsh, M., Mackenzie, J.M., Khromykh, A.A., Ee, K.-H., Wang, S.(2004) Structure 12: 1157-1163
- PubMed: 15242592
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2004.04.024
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1SFK - PubMed Abstract:
We have determined the crystal structure of the core (C) protein from the Kunjin subtype of West Nile virus (WNV), closely related to the NY99 strain of WNV, currently a major health threat in the U.S. WNV is a member of the Flaviviridae family of enveloped RNA viruses that contains many important human pathogens. The C protein is associated with the RNA genome and forms the internal core which is surrounded by the envelope in the virion. The C protein structure contains four alpha helices and forms dimers that are organized into tetramers. The tetramers form extended filamentous ribbons resembling the stacked alpha helices seen in HEAT protein structures.
- Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology, Singapore, Republic of Singapore. dokland@uab.edu
Organizational Affiliation: