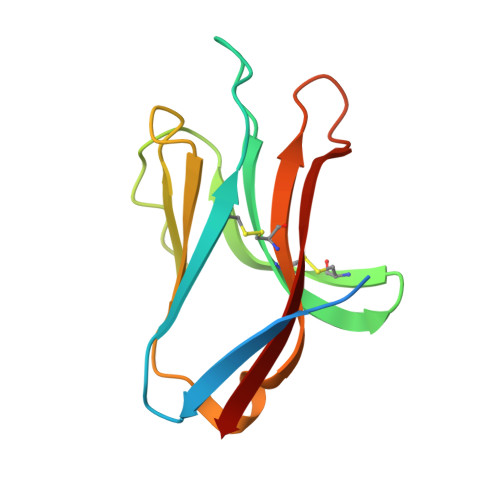
The Three-Dimensional Structure of the Human Nk Cell Receptor Nkp44, a Triggering Partner in Natural Cytotoxicity
Cantoni, C., Ponassi, M., Biassoni, R., Conte, R., Spallarossa, A., Moretta, A., Moretta, L., Bolognesi, M., Bordo, D.(2003) Structure 11: 725
- PubMed: 12791260
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0969-2126(03)00095-9
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1HKF - PubMed Abstract:
Natural killer (NK) cells direct cytotoxicity against tumor or virally infected cells. NK cell activation depends on a fine balance between inhibitory and activating receptors. NKp44 is a cytotoxicity activating receptor composed of one Ig-like extracellular domain, a transmembrane segment, and a cytoplasmic domain. The 2.2 A crystal structure shows that the NKp44 Ig domain forms a saddle-shaped dimer, where a charged surface groove protrudes from the core structure in each subunit. NKp44 Ig domain disulfide bridge topology defines a new Ig structural subfamily. The data presented are a first step toward understanding the molecular basis for ligand recognition by natural cytotoxicity receptors, whose key role in the immune system is established, but whose cellular ligands are still elusive.
- Dipartimento di Medicina Sperimentale, Università di Genova, Via L.B. Alberti 1, 16132 Genova, Italy.
Organizational Affiliation: