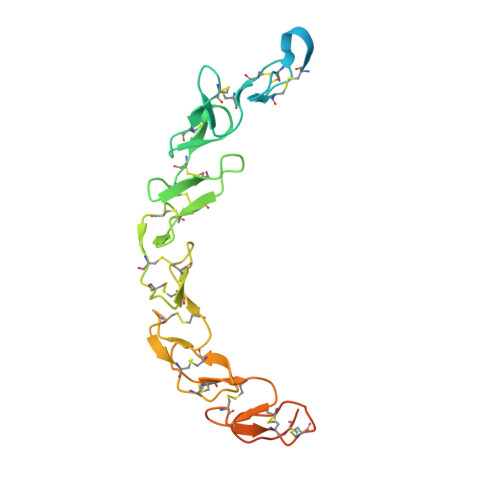
Structure of scavenger receptor SCARF1 and its interaction with lipoproteins.
Wang, Y., Xu, F., Li, G., Cheng, C., Yu, B., Zhang, Z., Kong, D., Chen, F., Liu, Y., Fang, Z., Cao, L., Yu, Y., Gu, Y., He, Y.(2024) Elife 13
- PubMed: 39541158
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.93428
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8HN0, 8HNA - PubMed Abstract:
SCARF1 (scavenger receptor class F member 1, SREC-1 or SR-F1) is a type I transmembrane protein that recognizes multiple endogenous and exogenous ligands such as modified low-density lipoproteins (LDLs) and is important for maintaining homeostasis and immunity. But the structural information and the mechanisms of ligand recognition of SCARF1 are largely unavailable. Here, we solve the crystal structures of the N-terminal fragments of human SCARF1, which show that SCARF1 forms homodimers and its epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like domains adopt a long-curved conformation. Then, we examine the interactions of SCARF1 with lipoproteins and are able to identify a region on SCARF1 for recognizing modified LDLs. The mutagenesis data show that the positively charged residues in the region are crucial for the interaction of SCARF1 with modified LDLs, which is confirmed by making chimeric molecules of SCARF1 and SCARF2. In addition, teichoic acids, a cell wall polymer expressed on the surface of gram-positive bacteria, are able to inhibit the interactions of modified LDLs with SCARF1, suggesting the ligand binding sites of SCARF1 might be shared for some of its scavenging targets. Overall, these results provide mechanistic insights into SCARF1 and its interactions with the ligands, which are important for understanding its physiological roles in homeostasis and the related diseases.
- State Key Laboratory of Systems Medicine for Cancer, Shanghai Cancer Institute, Renji Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China.
Organizational Affiliation: