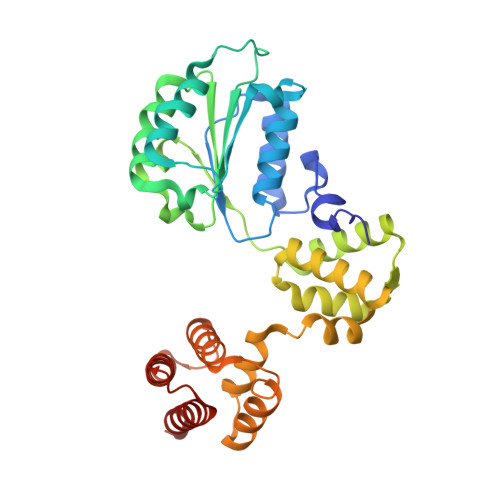
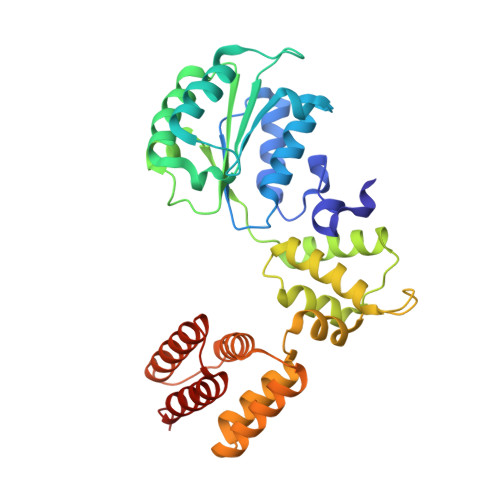
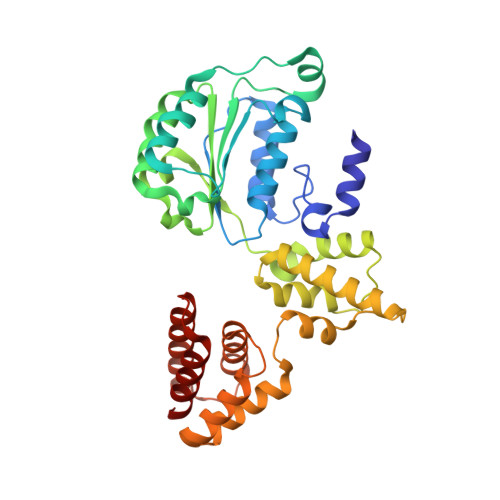
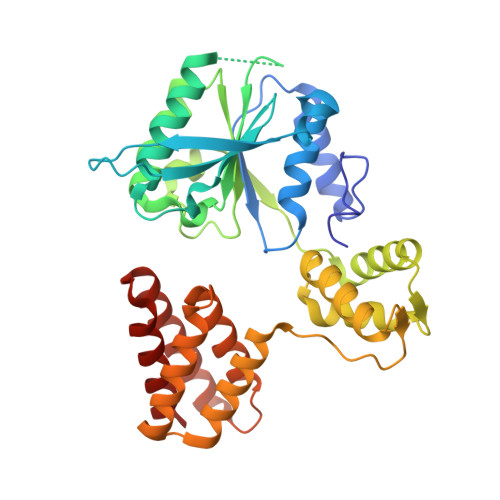
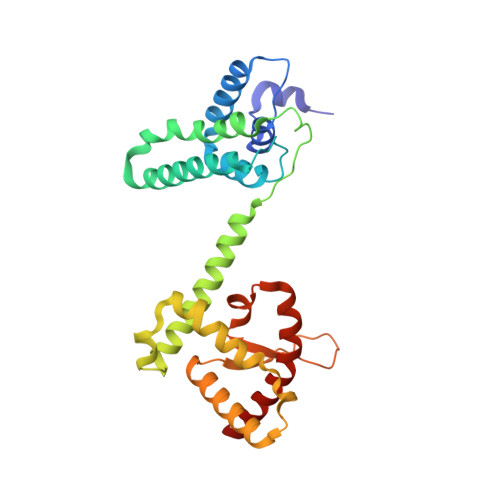
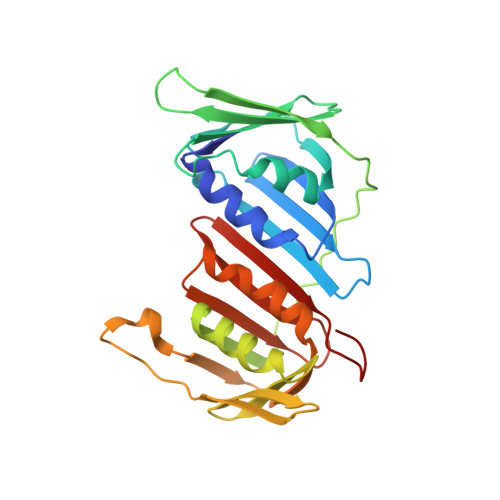
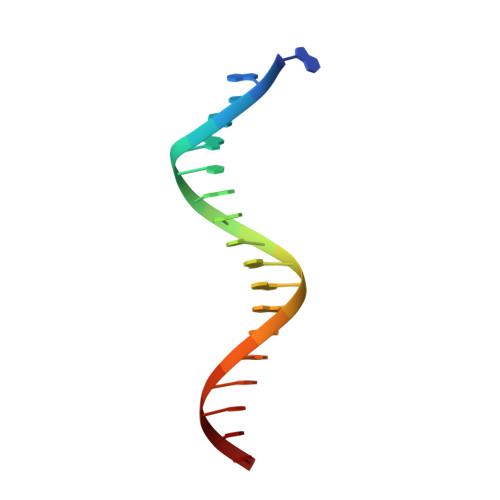
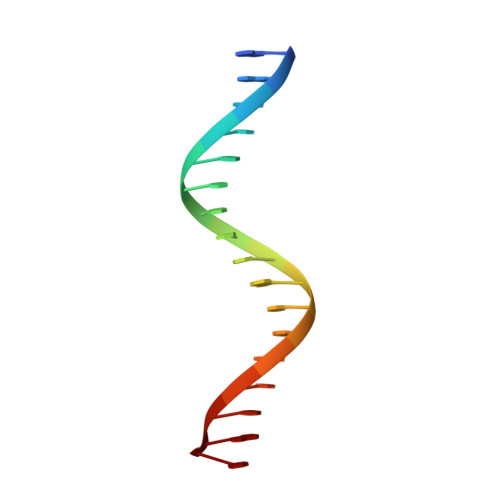
Mechanism of PCNA loading by Ctf18-RFC for leading-strand DNA synthesis.
Yuan, Z., Georgescu, R., Yao, N.Y., Yurieva, O., O'Donnell, M.E., Li, H.(2024) Science 385: eadk5901-eadk5901
- PubMed: 39088616
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.adk5901
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8TW7, 8TW8, 8TW9, 8TWA, 8TWB, 9B8R - PubMed Abstract:
The proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) clamp encircles DNA to hold DNA polymerases (Pols) to DNA for processivity. The Ctf18-RFC PCNA loader, a replication factor C (RFC) variant, is specific to the leading-strand Pol (Polε). We reveal here the underlying mechanism of Ctf18-RFC specificity to Polε using cryo-electron microscopy and biochemical studies. We found that both Ctf18-RFC and Polε contain specific structural features that direct PCNA loading onto DNA. Unlike other clamp loaders, Ctf18-RFC has a disordered ATPase associated with a diverse cellular activities (AAA+) motor that requires Polε to bind and stabilize it for efficient PCNA loading. In addition, Ctf18-RFC can pry prebound Polε off of DNA, then load PCNA onto DNA and transfer the PCNA-DNA back to Polε. These elements in both Ctf18-RFC and Polε provide specificity in loading PCNA onto DNA for Polε.
- Department of Structural Biology, Van Andel Institute, Grand Rapids, MI, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: