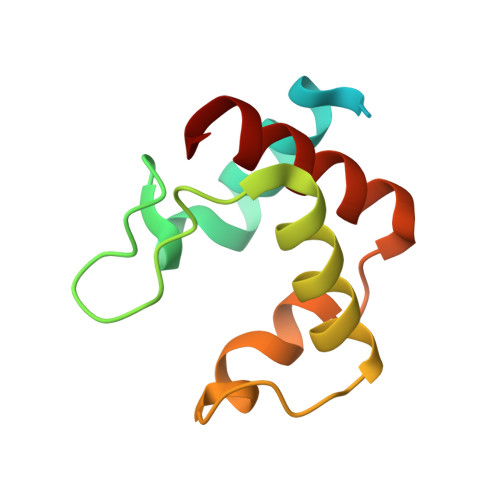
Relationship between the structure and physicochemical properties of cytochrome c 546/556 from the bacterium Thioalkalivibrio paradoxus ARh1.
Varfolomeeva, L.A., Solovieva, A.Y., Shipkov, N.S., Sluchanko, N.N., Boyko, K.M., Khrenova, M.G., Tikhonova, T.V., Popov, V.O.(2025) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 778: 152340-152340
- PubMed: 40669334
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2025.152340
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8YTS - PubMed Abstract:
An interplay between the structural and physicochemical properties of the monoheme cytochromes of type c has been extensively studied. However new proteins belonging to this diverse family continue to reveal some novel and unique features. Here, we present the 1.15 Å structure of the low-potential cytochrome c 546/556 from the bacterium Thioalkalivibrio paradoxus ARh1, which exhibits the prominent splitting of the Q bands in UV-visible spectra even at room temperature. The data obtained suggest that two conformations of the propionate 7 of the heme are responsible for the splitting of the Q bands. We propose that the degree of the splitting of the Q bands is correlated with the conformational lability of the heme propionates.
- Federal Research Centre «Fundamentals of Biotechnology» of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Leninsky prospect, 33, build. 2, Moscow, 119071, Russian Federation. Electronic address: l.varfolomeeva@fbras.ru.
Organizational Affiliation: