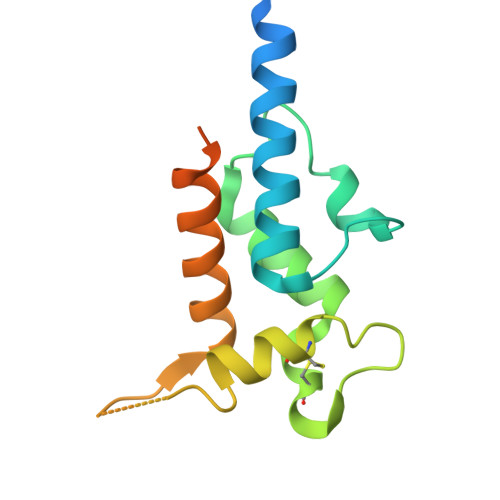
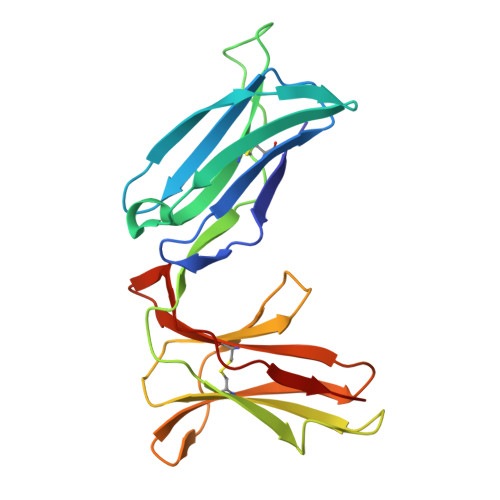
RIFINs displayed on malaria-infected erythrocytes bind KIR2DL1 and KIR2DS1.
Sakoguchi, A., Chamberlain, S.G., Morch, A.M., Widdess, M., Harrison, T.E., Dustin, M.L., Arase, H., Higgins, M.K., Iwanaga, S.(2025) Nature 643: 1363-1371
- PubMed: 40500441
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-025-09091-y
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9F2D, 9HML - PubMed Abstract:
Natural killer (NK) cells use inhibitory and activating immune receptors to differentiate between human cells and pathogens. Signalling by these receptors determines whether an NK cell becomes activated and destroys a target cell. In some cases, such as killer immunoglobulin-like receptors, immune receptors are found in pairs, with inhibitory and activating receptors containing nearly identical extracellular ligand-binding domains coupled to different intracellular signalling domains 1 . Previous studies showed that repetitive interspersed family (RIFIN) proteins, displayed on the surfaces of Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes, can bind to inhibitory immune receptors and dampen NK cell activation 2,3 , reducing parasite killing. However, no pathogen-derived ligand has been identified for any human activating receptor. Here we identified a clade of RIFINs that bind to inhibitory immune receptor KIR2DL1 more strongly than KIR2DL1 binds to the human ligand (MHC class I). This interaction mediates inhibitory signalling and suppresses the activation of KIR2DL1-expressing NK cells. We show that KIR2DL1-binding RIFINs are abundant in field-isolated strains from both Africa and Asia and reveal how the two RIFINs bind to KIR2DL1. The RIFIN binding surface of KIR2DL1 is conserved in the cognate activating immune receptor KIR2DS1. We find that KIR2DL1-binding RIFINs can also bind to KIR2DS1, resulting in the activation of KIR2DS1-expressing NK cells. This study demonstrates that activating killer immunoglobulin-like receptors can recruit NK cells to target a pathogen and reveals a potential role for activating immune receptors in controlling malaria infection.
- Department of Protozoology, Research Institute for Microbial Diseases, The University of Osaka, Suita, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: