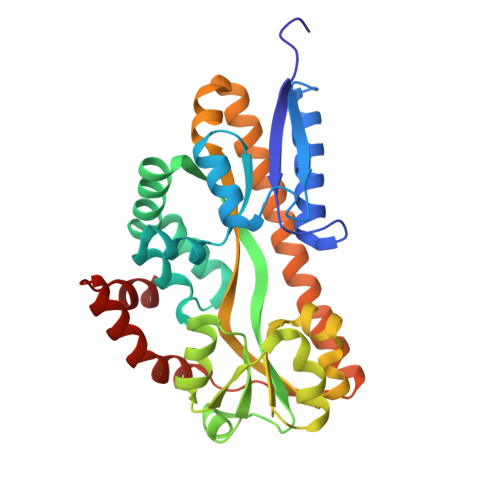
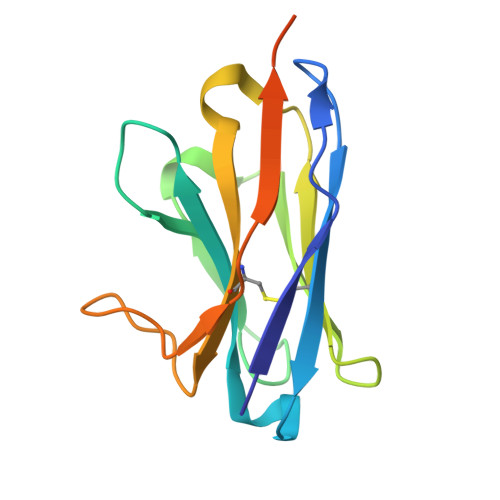
Allosteric substrate release by a sialic acid TRAP transporter substrate binding protein.
Schneberger, N., Hendricks, P., Peter, M.F., Gehrke, E., Binder, S.C., Koenig, P.A., Menzel, S., Thomas, G.H., Hagelueken, G.(2024) Commun Biol 7: 1559-1559
- PubMed: 39580575
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-024-07263-6
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9FVB, 9FVC, 9FVE - PubMed Abstract:
The tripartite ATP-independent periplasmic (TRAP) transporters enable Vibrio cholerae and Haemophilus influenzae to acquire sialic acid, aiding their colonization of human hosts. This process depends on SiaP, a substrate-binding protein (SBP) that captures and delivers sialic acid to the transporter. We identified 11 nanobodies that bind specifically to the SiaP proteins from H. influenzae (HiSiaP) and V. cholerae (VcSiaP). Two nanobodies inhibited sialic acid binding. Detailed structural and biophysical studies of one nanobody-SBP complex revealed an allosteric inhibition mechanism, preventing ligand binding and releasing pre-bound sialic acid. A hydrophobic surface pocket of the SBP is crucial for the allosteric mechanism and for the conformational rearrangement that occurs upon binding of sialic acid to the SBP. Our findings provide new clues regarding the mechanism of TRAP transporters, as well as potential starting points for novel drug design approaches to starve these human pathogens of important host-derived molecules.
- Institute of Structural Biology, University of Bonn, Venusberg-Campus 1, 53127, Bonn, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: