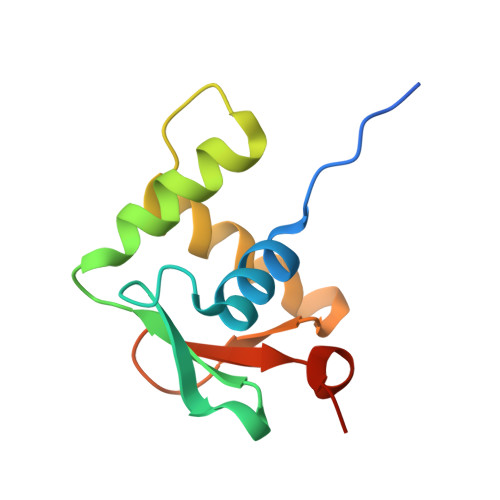
Structural analysis of Spi-B DNA-binding Ets domain recognizing 5'-AGAA-3' and 5'-GGAA-3' sequences.
Nonaka, Y., Hoshino, K., Nakamura, T., Kamitori, S.(2025) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 749: 151354-151354
- PubMed: 39892964
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2025.151354
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9J1N, 9J1O - PubMed Abstract:
Plasmacytoid dendritic cells produce large amounts of type-I interferon (IFN-I) upon sensing nucleic acid components of pathogens by Toll-like receptors (TLR7 and TLR9). The transcription factor Spi-B has the DNA-binding Ets domain, and transactivates the Ifna4 promoter co-operatively with IFN regulatory factor-7 (IRF-7) for TLR7/TLR9-induced IFN-I production. Spi-B associates with IRF-7, and activates transcription by binding to the 5'-AGAA-3' sequence, being different from 5'-GGAA-3', known as the Ets domain recognition sequence. To understand the molecular mechanism for the co-operative transactivation of the Ifna4 promoter by Spi-B and IRF-7, we performed X-ray structural determination of the Spi-B Ets domain in complex with target DNAs, including 5'-AGAA-3' and 5'-GGAA-3' sequences. Furthermore, we conducted a modeling study of the complex of the Spi-B and IRF-7 with Ifna4 promoter DNA. X-ray structures showed that the binding of the Spi-B Ets domain induces a kink in DNA at the recognition sequence, and a more kinked DNA structure was observed in 5'-AGAA-3' than 5'-GGAA-3'. A modeling study showed that the Spi-B-induced kinked DNA structure in 5'-AGAA-3' is favorable for Spi-B and IRF-7 to approach each other for association on DNA.
Organizational Affiliation:
International Institute of Rare Sugar Research and Education, Kagawa University, Takamatsu, Kagawa, 760-8521, Japan; Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine, Kagawa University, 1750-1 Ikenobe, Miki-cho, Kita-gun, Kagawa, 761-0793, Japan.