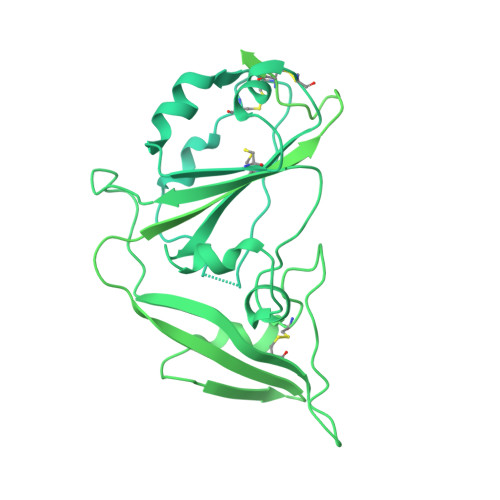
HKU5 bat merbecoviruses engage bat and mink ACE2 as entry receptors.
Madel Alfajaro, M., Keeler, E.L., Li, N., Catanzaro, N.J., Teng, I.T., Zhao, Z., Grunst, M.W., Yount, B., Schafer, A., Wang, D., Kim, A.S., Synowiec, A., Pena-Hernandez, M.A., Zepeda, S., Arinola, R., Kaur, R., Menasche, B.L., Wei, J., Russell, G.A., Huck, J., Song, J., Ring, A., Iwasaki, A., Jangra, R.K., Lee, S., Martinez, D.R., Mothes, W., Uchil, P.D., Doench, J.G., Spaulding, A.B., Baric, R.S., Serebryannyy, L., Tsybovsky, Y., Zhou, T., Douek, D.C., Wilen, C.B.(2025) Nat Commun 16: 6822-6822
- PubMed: 40707428
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-61583-7
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9MV0 - PubMed Abstract:
Identifying receptors for bat coronaviruses is critical for spillover risk assessment, countermeasure development, and pandemic preparedness. While Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) uses DPP4 for entry, the receptors of many MERS-related betacoronaviruses remain unknown. The bat merbecovirus HKU5 was previously shown to have an entry restriction in human cells. Using both pseudotyped and full-length virus, we show that HKU5 uses Pipistrellus abramus bat ACE2 but not human ACE2 or DPP4 as a receptor. Cryo-electron microscopy analysis of the virus-receptor complex and structure-guided mutagenesis reveal a spike and ACE2 interaction that is distinct from other ACE2-using coronaviruses. MERS-CoV vaccine sera poorly neutralize HKU5 informing pan-merbecovirus vaccine design. Notably, HKU5 can also engage American mink and stoat ACE2, revealing mustelids as potential intermediate hosts. These findings highlight the versatility of merbecovirus receptor use and underscore the need for continued surveillance of bat and mustelid species.
- Department of Laboratory Medicine, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: