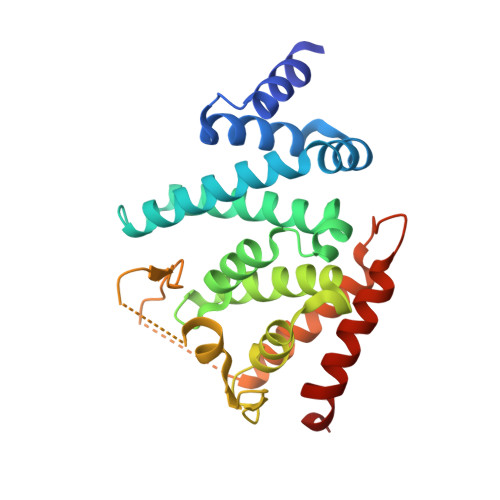
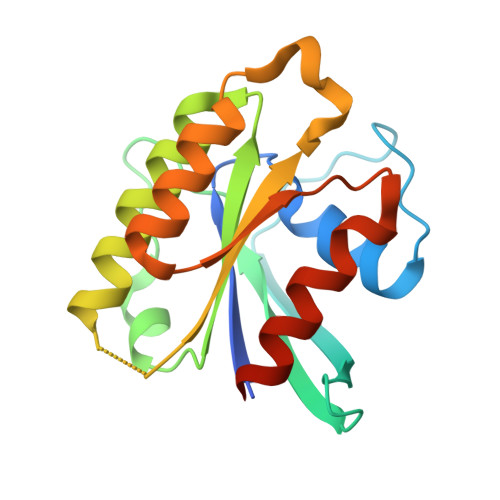
The GTPase kappa B-Ras is an essential subunit of the RalGAP tumor suppressor complex.
Rasche, R., Apken, L.H., Titze, S., Michalke, E., Singh, R.K., Oeckinghaus, A., Kummel, D.(2025) J Biological Chem 301: 110460-110460
- PubMed: 40619001
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2025.110460
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9QU1 - PubMed Abstract:
κB-Ras1 and κB-Ras2 are small GTPases with non-canonical features that act as tumor suppressors downstream of Ras. Via interaction with the RalGAP (GTPase activating protein) complex, they limit activity of Ral GTPases and restrict anchorage-independent proliferation. We here present the crystal structure of κB-Ras1 in complex with the N-terminal domain of RGα2. The structure suggests a mechanism of intrinsic GTP hydrolysis of κB-Ras1 that relies on a scaffolding function of the GTPase rather than on catalytic residues, which we confirm by mutational analysis. The interaction with RGα2 is nucleotide-independent and does not involve κB-Ras1 switch regions, which establishes κB-Ras proteins as a constitutive third subunit of RalGAP complexes. Functional studies demonstrate that κB-Ras proteins are not required for RalGAP catalytic activity in vitro, but for functionality in vivo. We propose that κB-Ras may thus act as regulator of RalGAP localization and thereby control the Ras/Ral signaling pathway.
- Institute of Biochemistry, University of Münster, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: