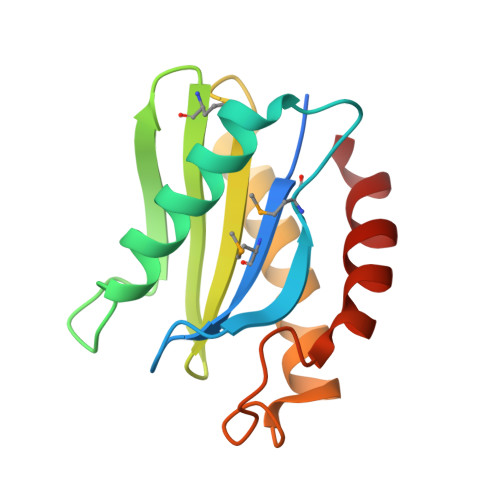
A novel snare N-terminal domain revealed by the crystal structure of Sec22b.
Gonzalez Jr., L.C., Weis, W.I., Scheller, R.H.(2001) J Biological Chem 276: 24203-24211
- PubMed: 11309394
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M101584200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1IFQ - PubMed Abstract:
Intra-cellular membrane fusion is facilitated by the association of SNAREs from opposite membranes into stable alpha-helical bundles. Many SNAREs, in addition to their alpha-helical regions, contain N-terminal domains that likely have essential regulatory functions. To better understand this regulation, we have determined the 2.4-A crystal structure of the 130-amino acid N-terminal domain of mouse Sec22b (mSec22b), a SNARE involved in endoplasmic reticulum/Golgi membrane trafficking. The domain consists of a mixed alpha-helical/beta-sheet fold that resembles a circular permutation of the actin/poly-proline binding protein, profilin, and the GAF/PAS family of regulatory modules. The structure is distinct from the previously characterized N-terminal domain of syntaxin 1A, and, unlike syntaxin 1A, the N-terminal domain of mSec22b has no effect on the rate of SNARE assembly in vitro. An analysis of surface conserved residues reveals a potential protein interaction site. Key residues in this site are distinct in two mammalian Sec22 variants that lack SNARE domains. Finally, sequence analysis indicates that a similar domain is likely present in the endosomal/lysosomal SNARE VAMP7.
- Department of Molecular and Cellular Physiology, Howard Hughes Medical Institute and the Department of Structural Biology, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, California 94305, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: