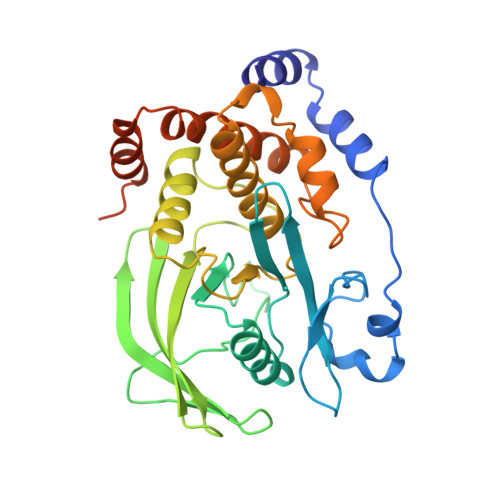
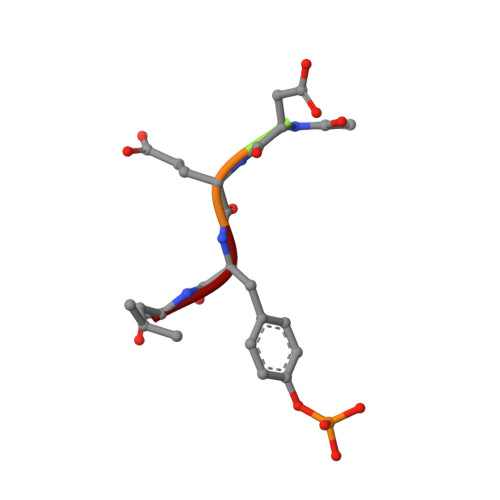
Structural basis for phosphotyrosine peptide recognition by protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B.
Jia, Z., Barford, D., Flint, A.J., Tonks, N.K.(1995) Science 268: 1754-1758
- PubMed: 7540771
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.7540771
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1PTT, 1PTU, 1PTV - PubMed Abstract:
The crystal structures of a cysteine-215-->serine mutant of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B complexed with high-affinity peptide substrates corresponding to an autophosphorylation site of the epidermal growth factor receptor were determined. Peptide binding to the protein phosphatase was accompanied by a conformational change of a surface loop that created a phosphotyrosine recognition pocket and induced a catalytically competent form of the enzyme. The phosphotyrosine side chain is buried within the period and anchors the peptide substrate to its binding site. Hydrogen bonds between peptide main-chain atoms and the protein contribute to binding affinity, and specific interactions of acidic residues of the peptide with basic residues on the surface of the enzyme confer sequence specificity.
- Laboratory of Molecular Biophysics, University of Oxford, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: