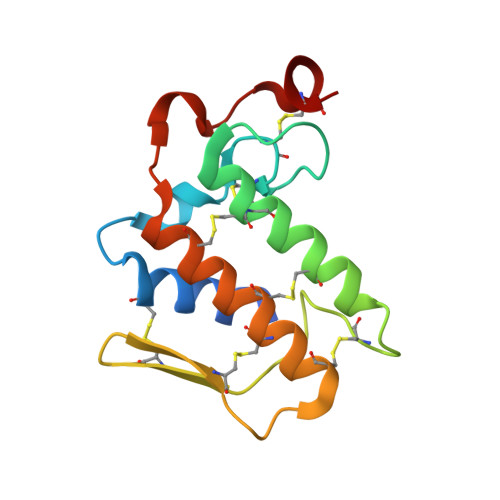
Crystal structure of a novel phospholipase A(2) from Naja naja sagittifera with a strong anticoagulant activity
Jabeen, T., Singh, N., Singh, R.K., Ethayathulla, A.S., Sharma, S., Srinivasan, A., Singh, T.P.(2005) Toxicon 46: 865-875
- PubMed: 16269164
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2005.08.008
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1YXH - PubMed Abstract:
This is the first PLA(2) crystal structure from group I that shows a strong anticoagulant property. The monomeric PLA(2) was purified from the venom of Naja naja sagittifera (Indian cobra). Its amino acid sequence has been determined using cDNA technique. The amino acid sequence of sPLA(2) contains three positively charged and two negatively charged residues in the segment 54-71 (numbering scheme of sPLA(2)) thus giving this region an overall cationic amphiphilic surface. This suggested the presence of an anticoagulant activity in sPLA(2). The enzyme was crystallized using hanging drop vapour diffusion method in the presence of calcium chloride. The crystals belong to space group P4(1) with cell dimensions of a=b=42.0A, c=65.9A. The X-ray crystal structure was determined at 1.8A resolution using molecular replacement method and refined to an R value of 0.179 for 10,023 reflections. The overall scaffolding of sPLA(2) is essentially similar to those observed for other group I PLA(2)s. However, the conformations of various surface loops were found to be significantly different. The most significant observation pertains to the anticoagulant loop in which both the acidic residues are engaged in intramolecular interactions whereas all the three basic residues are free to interact with other molecules. This makes the sPLA(2) a potentially strong anticoagulating molecule.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biophysics, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Ansari Nagar, New Delhi 110029, India.