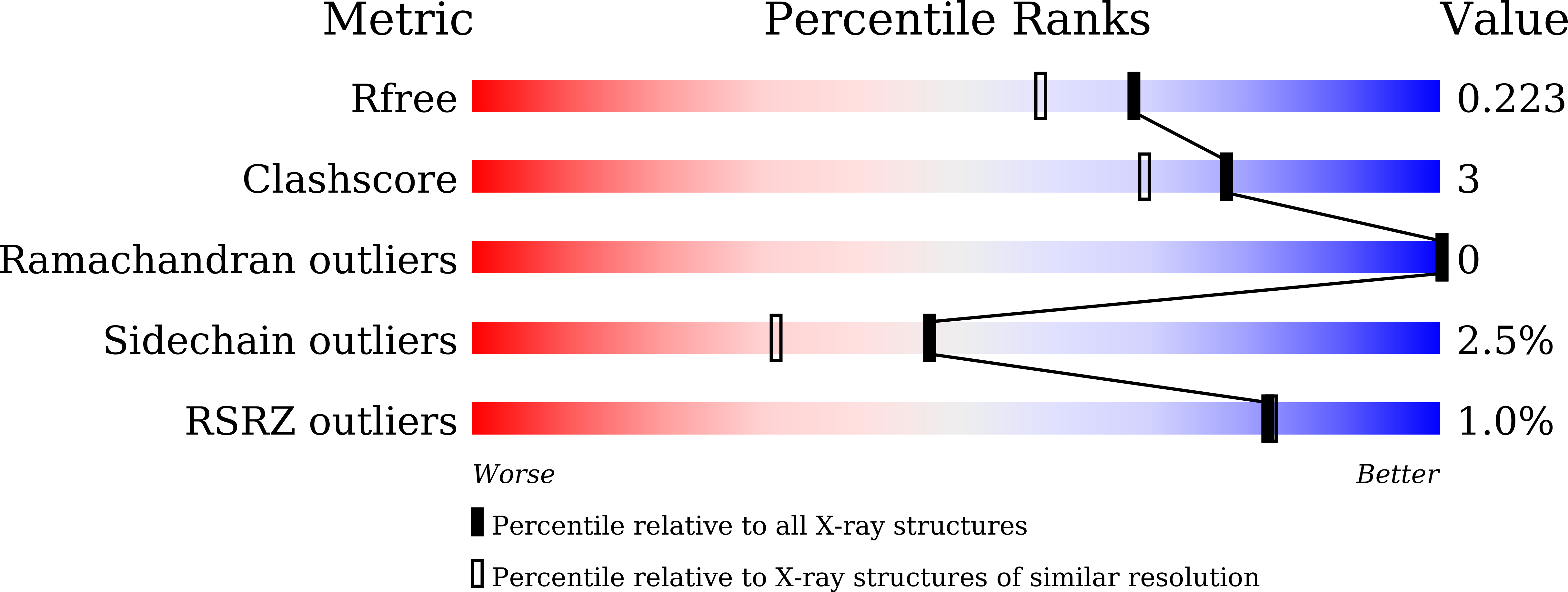
Biochemical and structural studies of Mycobacterium smegmatis MutT1, a sanitization enzyme with unusual modes of association
Arif, S.M., Patil, A.G., Varshney, U., Vijayan, M.(2017) Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol 73: 349-364
- PubMed: 28375146
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2059798317002534
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5GG5, 5GG6, 5GG7, 5GG8, 5GG9, 5GGA, 5GGB, 5GGC, 5GGD - PubMed Abstract:
Mycobacterium smegmatis MutT1, which is made up of a Nudix domain (domain 1) and a histidine phosphatase domain (domain 2), efficiently hydrolyses 8-oxo-GTP and 8-oxo-dGTP to the corresponding nucleoside diphosphates and phosphate in the presence of magnesium ions. Domain 1 alone hydrolyses nucleoside triphosphates less efficiently. Under high concentrations and over long periods, the full-length enzyme as well as domain 1 catalyses the hydrolysis of the nucleoside triphosphates to the respective nucleoside monophosphates and pyrophosphate. The role of domain 2 appears to be limited to speeding up the reaction. Crystal structures of the apoenzyme and those of ligand-bound enzyme prepared in the presence of 8-oxo-GTP or 8-oxo-dGTP and different concentrations of magnesium were determined. In all of the structures except one, the molecules arrange themselves in a head-to-tail fashion in which domain 1 is brought into contact with domain 2 (trans domain 2) of a neighbouring molecule. The binding site for NTP (site A) is almost exclusively made up of residues from domain 1, while those for NDP (site B) and NMP (site C) are at the interface between domain 1 and trans domain 2 in an unusual instance of intermolecular interactions leading to binding sites. Protein-ligand interactions at site A lead to a proposal for the mechanism of hydrolysis of NTP to NDP and phosphate. A small modification in site A in the crystal which does not exhibit the head-to-tail arrangement appears to facilitate the production of NMP and pyrophosphate from NTP. The two arrangements could be in dynamic equilibrium in the cellular milieu.
Organizational Affiliation:
Molecular Biophysics Unit, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560 012, India.