A structural model for microtubule minus-end recognition and protection by CAMSAP proteins.
Atherton, J., Jiang, K., Stangier, M.M., Luo, Y., Hua, S., Houben, K., van Hooff, J.J.E., Joseph, A.P., Scarabelli, G., Grant, B.J., Roberts, A.J., Topf, M., Steinmetz, M.O., Baldus, M., Moores, C.A., Akhmanova, A.(2017) Nat Struct Mol Biol 24: 931-943
- PubMed: 28991265
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.3483
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
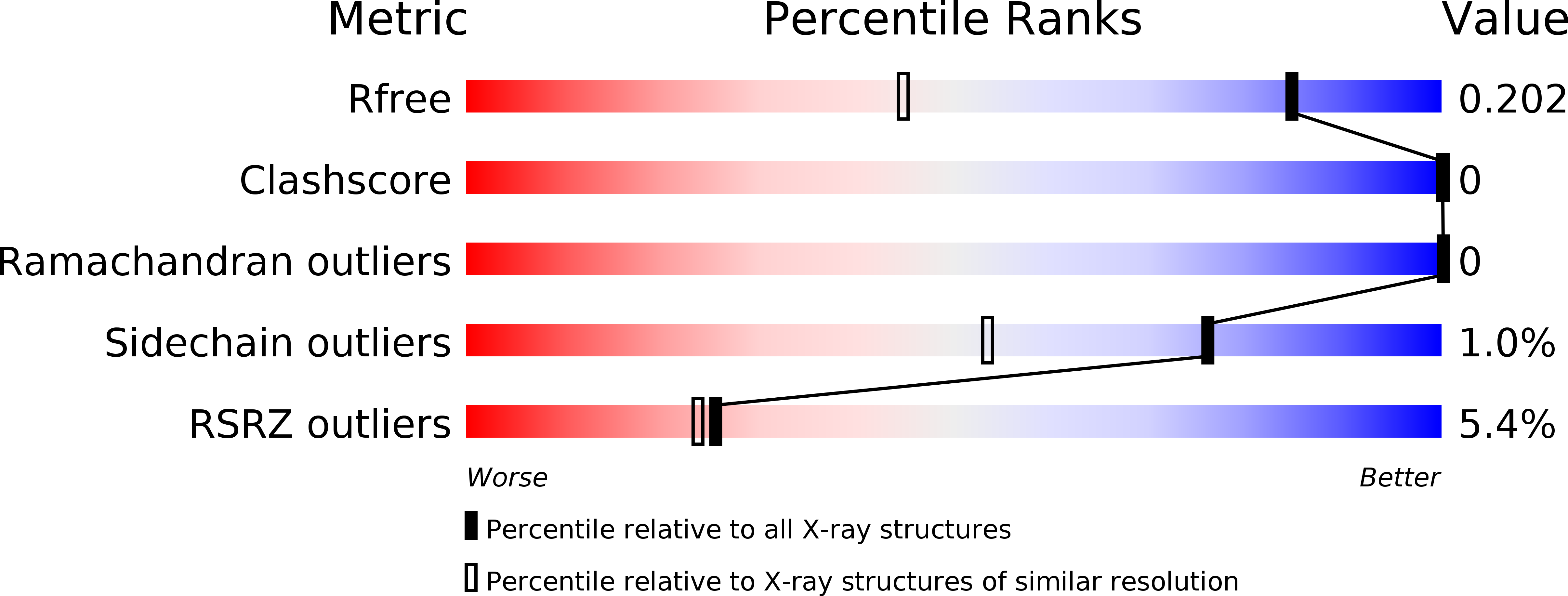
5LZN, 5M50, 5M54, 5M5C - PubMed Abstract:
CAMSAP and Patronin family members regulate microtubule minus-end stability and localization and thus organize noncentrosomal microtubule networks, which are essential for cell division, polarization and differentiation. Here, we found that the CAMSAP C-terminal CKK domain is widely present among eukaryotes and autonomously recognizes microtubule minus ends. Through a combination of structural approaches, we uncovered how mammalian CKK binds between two tubulin dimers at the interprotofilament interface on the outer microtubule surface. In vitro reconstitution assays combined with high-resolution fluorescence microscopy and cryo-electron tomography suggested that CKK preferentially associates with the transition zone between curved protofilaments and the regular microtubule lattice. We propose that minus-end-specific features of the interprotofilament interface at this site serve as the basis for CKK's minus-end preference. The steric clash between microtubule-bound CKK and kinesin motors explains how CKK protects microtubule minus ends against kinesin-13-induced depolymerization and thus controls the stability of free microtubule minus ends.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Structural and Molecular Biology, Birkbeck, University of London, London, UK.