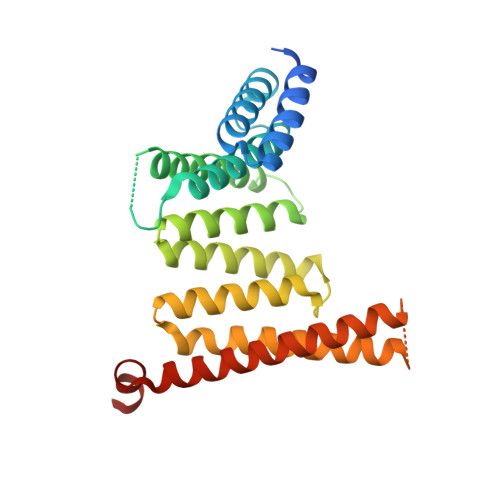
Structural basis for histone H3 recognition by NASP in Arabidopsis.
Liu, Y., Chen, L., Wang, N., Wu, B., Bao, H., Huang, H.(2022) J Integr Plant Biol 64: 2309-2313
- PubMed: 35587028
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.13277
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7W5M - PubMed Abstract:
The structural basis for histone recognition by the histone chaperone nuclear autoantigenic sperm protein (NASP) remains largely unclear. Here, we showed that Arabidopsis thaliana AtNASP is a monomer and displays robust nucleosome assembly activity in vitro. Examining the structure of AtNASP complexed with a histone H3 α3 peptide revealed a binding mode that is conserved in human NASP. AtNASP recognizes the H3 N-terminal region distinct from human NASP. Moreover, AtNASP forms a co-chaperone complex with ANTI-SILENCING FUNCTION 1 (ASF1) by binding to the H3 N-terminal region. Therefore, we deciphered the structure of AtNASP and the basis of the AtNASP-H3 interaction.
- Key Laboratory of Molecular Design for Plant Cell Factory of Guangdong Higher Education Institutes, Department of Biology, School of Life Sciences, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, 518055, China.
Organizational Affiliation: