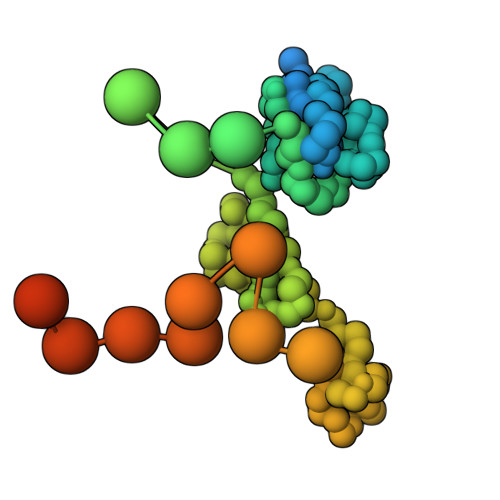
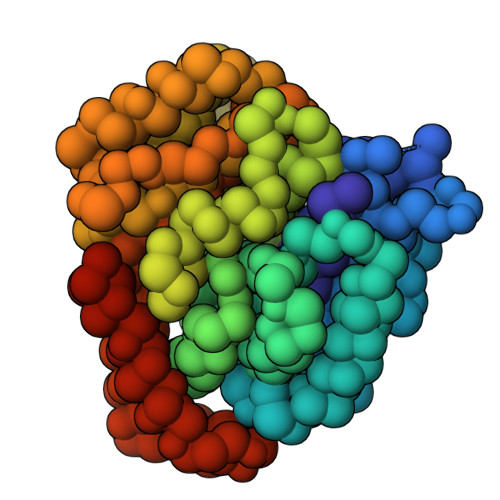
Doublecortin engages the microtubule lattice through a cooperative binding mode involving its C-terminal domain
Rafiei A, Lee L, Crowder A, Saltzberg D, Sali A, Brouhard G, Schreimer DC(2022) Elife 11: e66975
- PubMed: 35485925
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.66975
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9A0Z, 9A10, 9A11, 9A12 - PubMed Abstract:
Doublecortin (DCX) is a microtubule (MT)-associated protein that regulates MT structure and function during neuronal development and mutations in DCX lead to a spectrum of neurological disorders. The structural properties of MT-bound DCX that explain these disorders are incompletely determined. Here, we describe the molecular architecture of the DCX-MT complex through an integrative modeling approach that combines data from X-ray crystallography, cryo-electron microscopy, and a high-fidelity chemical crosslinking method. We demonstrate that DCX interacts with MTs through its N-terminal domain and induces a lattice-dependent self-association involving the C-terminal structured domain and its disordered tail, in a conformation that favors an open, domain-swapped state. The networked state can accommodate multiple different attachment points on the MT lattice, all of which orient the C-terminal tails away from the lattice. As numerous disease mutations cluster in the C-terminus, and regulatory phosphorylations cluster in its tail, our study shows that lattice-driven self-assembly is an important property of DCX.
- Department of Chemistry, University of Calgary, Calgary, Canada.
Organizational Affiliation: