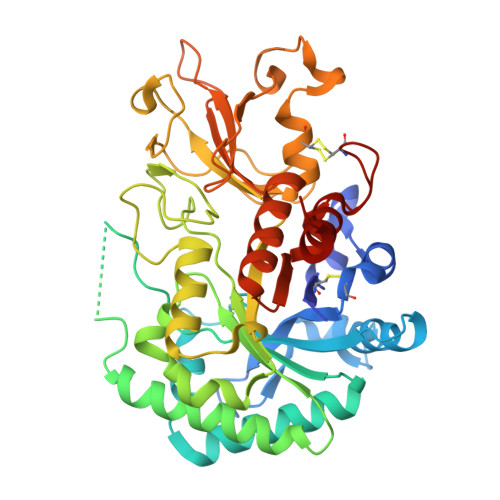
Structural and functional significance of Aedes aegypti AgBR1 flavivirus immunomodulator.
Martinez-Castillo, A., Barriales, D., Azkargorta, M., Zalamea, J.D., Arda, A., Jimenez-Barbero, J., Gonzalez-Lopez, M., Aransay, A.M., Marin-Lopez, A., Fikrig, E., Elortza, F., Anguita, J., Abrescia, N.G.A.(2025) J Virol 99: e0187824-e0187824
- PubMed: 40272158
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.01878-24
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9G3Q - PubMed Abstract:
Zika virus (ZIKV), an arbovirus, relies on mosquitoes as vectors for its transmission. During blood feeding, mosquitoes inoculate saliva containing various proteins. Recently, AgBR1, an Aedes aegypti salivary gland protein, has gained attention for its immunomodulatory potential, along with another protein, called NeSt1. We have determined the crystal structure of AgBR1 at 1.2 Å resolution. Despite its chitinase-like fold, we demonstrated that AgBR1 does not bind to chitobiose or chitinhexaose, while a key mutation in the catalytic site abrogates enzymatic activity, suggesting that the protein's function has been repurposed. Our study also shows that AgBR1 and NeSt1, when presented to murine primary macrophages, alter cellular pathways related to virus entry by endocytosis, immune response, and cell proliferation. AgBR1 (and NeSt1) do not directly bind to the Zika virus or modulate its replication. We propose that their immunomodulatory effects on Zika virus transmission are through regulation of host-cell response, a consequence of evolutionary cross talk and virus opportunism. These structural and functional insights are prerequisites for developing strategies to halt the spread of mosquito-borne disease.IMPORTANCEOur study informs on the structural and functional significance of a mosquito salivary gland protein, AgBR1 (along with another protein called NeSt1), in the transmission of the Zika virus (ZIKV), a mosquito-borne virus that has caused global health concerns. By analyzing AgBR1's three-dimensional structure in combination with cellular and interaction studies, we discovered that AgBR1 does not function like typical proteins in its family-it does not degrade sugars. However, we show that it primes immune cells in a way that could help the virus enter cells more easily but not by interacting with the virus or altering viral replication. This finding is significant because it reveals how mosquito proteins, repurposed by evolution, can influence virus transmission without the virus's direct presence. Understanding how proteins like AgBR1 work could guide the development of new strategies to prevent Zika virus spread, with potential relevance for other mosquito-borne viruses.
- Structure and Cell Biology of Viruses Lab, Center for Cooperative Research in Biosciences (CIC bioGUNE) - Basque Research and Technology Alliance (BRTA), Derio, Spain.
Organizational Affiliation: