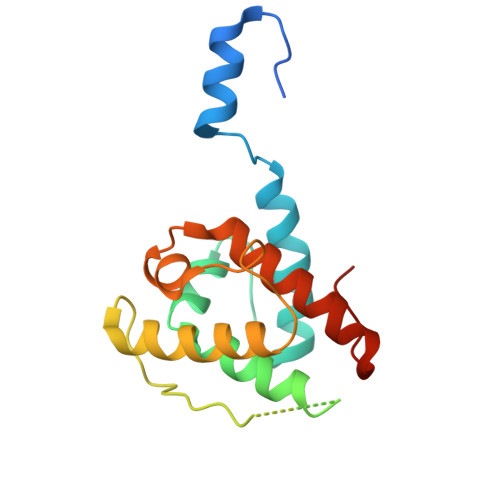
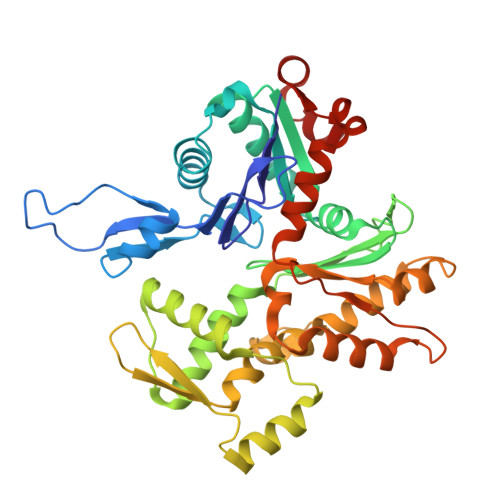
Dimerization of GAS2 mediates crosslinking of microtubules and F-actin.
An, J., Imasaki, T., Narita, A., Niwa, S., Sasaki, R., Makino, T., Nitta, R., Kikkawa, M.(2025) EMBO J 44: 2997-3024
- PubMed: 40169809
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s44318-025-00415-2
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9KBW, 9KBX - PubMed Abstract:
The spectraplakin family protein GAS2 was originally identified as a growth arrest-specific protein, and recent studies have revealed its involvement in multiple cellular processes. Its dual interaction with actin filaments and microtubules highlights its essential role in cytoskeletal organization, such as cell division, apoptosis, and possibly tumorigenesis. However, the structural basis of cytoskeletal dynamics regulation by GAS2 remains unclear. In this study, we present cryo-electron microscopy structures of the GAS2 type 3 calponin homology domain (CH3) in complex with F-actin at 2.8 Å resolution, thus solving the first type CH3 domain structure bound to F-actin and confirming its actin-binding activity. We also provide the first near-atomic resolution cryo-EM structure of the GAS2-GAR domain bound to microtubules and identify conserved microtubule-binding residues. Our biochemical experiments show that GAS2 promotes microtubule nucleation and polymerization, and that its C-terminal region is essential for dimerization, bundling of both F-actin and microtubules, and microtubule nucleation. As mutations leading to expression of C-terminally truncated GAS2 have been linked to hearing loss, these findings suggest that the disruption of GAS2-dependent cytoskeletal organisation could underlie auditory dysfunction.
- Department of Cell Biology and Anatomy, Graduate School of Medicine, The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: