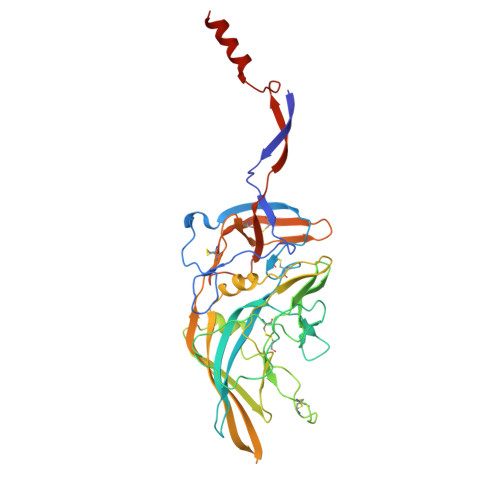
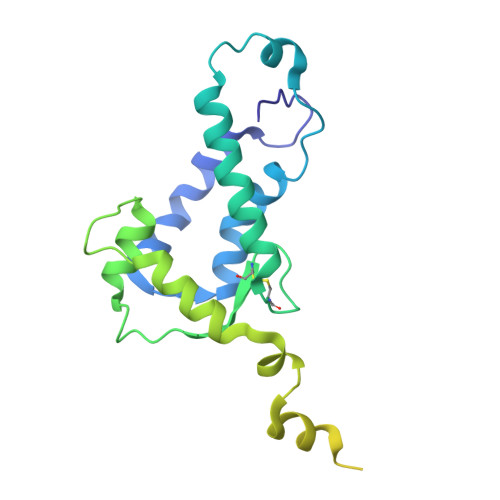
Human endogenous retrovirus K (HERV-K) envelope structures in pre- and postfusion by cryo-EM.
Shek, J., Sun, C., Wilson, E.M., Moadab, F., Hastie, K.M., Rajamanickam, R.R., Penalosa, P.J., Harkins, S.S., Parekh, D., Hariharan, C., Zyla, D.S., Yu, C., Shaffer, K.C.L., Lewis, V.I., Avalos, R.D., Mustelin, T., Saphire, E.O.(2025) Sci Adv 11: eady8168-eady8168
- PubMed: 40864726
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.ady8168
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9MLA, 9MLK, 9O4F - PubMed Abstract:
Human endogenous retroviruses (HERVs) are remnants of ancient infections that comprise ~8% of the human genome. The HERV-K envelope glycoprotein (Env) is aberrantly expressed in cancers, autoimmune disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases, and is targeted by patients' own antibodies. However, a lack of structural information has limited molecular and immunological studies of the roles of HERVs in disease. Here, we present cryo-electron microscopy structures of stabilized HERV-K Env in the prefusion conformation, revealing a distinct fold and architecture compared to HIV and simian immunodeficiency virus. We also generated and characterized a panel of monoclonal antibodies with subunit and conformational specificity, serving as valuable research tools. These antibodies enabled structure determination of the postfusion conformation of HERV-K Env, including its unique "tether" helix, and antibody-bound prefusion Env. Together, these results provide a structural framework that opens the door to mechanistic studies of HERV-K Env and tools for its evaluation as a potential therapeutic target.
- Center for Vaccine Innovation, La Jolla Institute for Immunology, La Jolla, CA 92037, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: