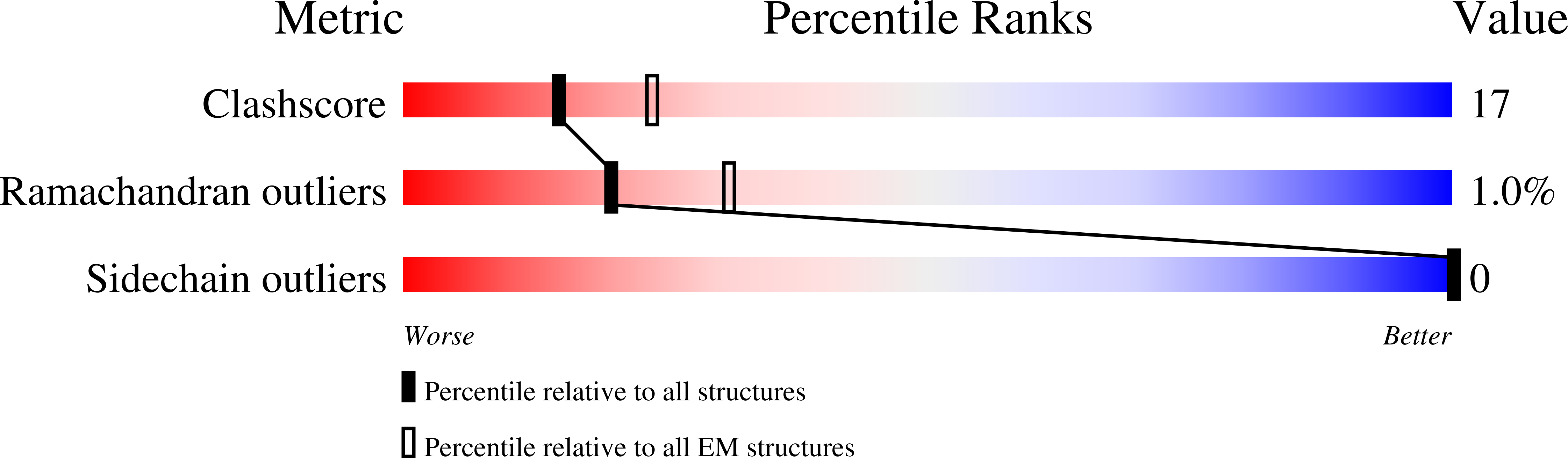The structure and oxidation of the eye lens chaperone alpha A-crystallin.
Kaiser, C.J.O., Peters, C., Schmid, P.W.N., Stavropoulou, M., Zou, J., Dahiya, V., Mymrikov, E.V., Rockel, B., Asami, S., Haslbeck, M., Rappsilber, J., Reif, B., Zacharias, M., Buchner, J., Weinkauf, S.(2019) Nat Struct Mol Biol 26: 1141-1150
- PubMed: 31792453
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41594-019-0332-9
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6T1R - PubMed Abstract:
The small heat shock protein αA-crystallin is a molecular chaperone important for the optical properties of the vertebrate eye lens. It forms heterogeneous oligomeric ensembles. We determined the structures of human αA-crystallin oligomers by combining cryo-electron microscopy, cross-linking/mass spectrometry, NMR spectroscopy and molecular modeling. The different oligomers can be interconverted by the addition or subtraction of tetramers, leading to mainly 12-, 16- and 20-meric assemblies in which interactions between N-terminal regions are important. Cross-dimer domain-swapping of the C-terminal region is a determinant of αA-crystallin heterogeneity. Human αA-crystallin contains two cysteines, which can form an intramolecular disulfide in vivo. Oxidation in vitro requires conformational changes and oligomer dissociation. The oxidized oligomers, which are larger than reduced αA-crystallin and destabilized against unfolding, are active chaperones and can transfer the disulfide to destabilized substrate proteins. The insight into the structure and function of αA-crystallin provides a basis for understanding its role in the eye lens.
Organizational Affiliation:
Center for Integrated Protein Science Munich at the Department Chemie, Technische Universität München, Garching, Germany.